Edge Computing – Bringing the Cloud to You
Content Map
More chaptersEven if you are a beginner at IT, you must have heard of Cloud computing, where data is stored in a Cloud server and be processed through the Internet.
Even if you are a beginner at IT, you must have heard of Cloud computing, where data is stored in a Cloud server and be processed through the Internet.
Think of any centralized service – that is an example of Cloud services. For example, Gmail, Office 365, Youtube, Facebook, etc. Cloud exists everywhere and is a vital part of everyday life.
Artificial Intelligence such as Siri, Alexa, is also built based on Cloud computing.
The only disadvantage of Cloud computing however, is that most of our Cloud services are provided by the big IT players such as Google, Amazon, Apple… that might not be situated near the source of data.
With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) however, Cloud is not optimal anymore due to the distance data has to travel which results in latency and ping. Companies then realized that they need something faster – something close and personal – something at the “edge” of the Internet.
Therefore, Edge Computing was born.

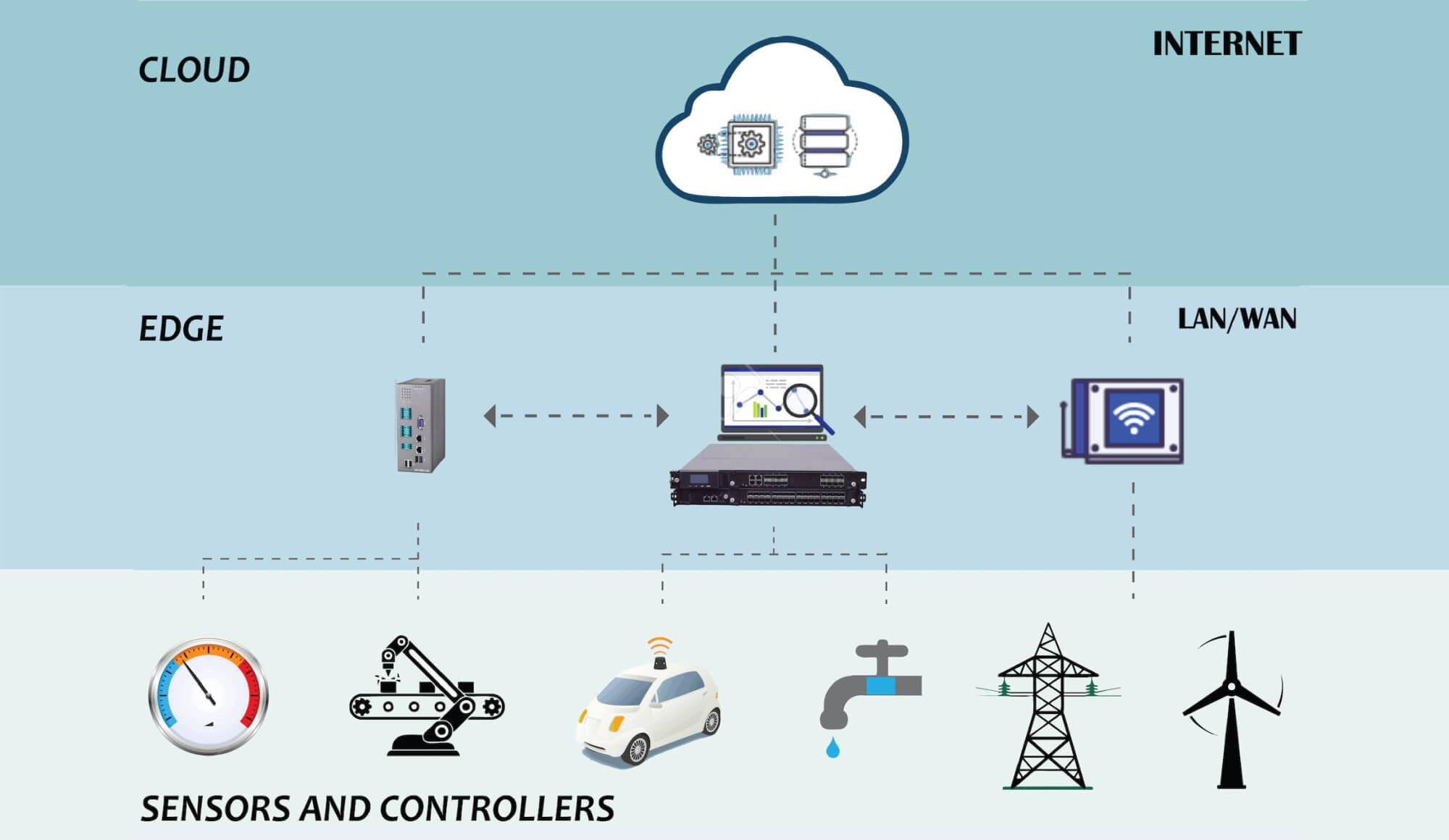
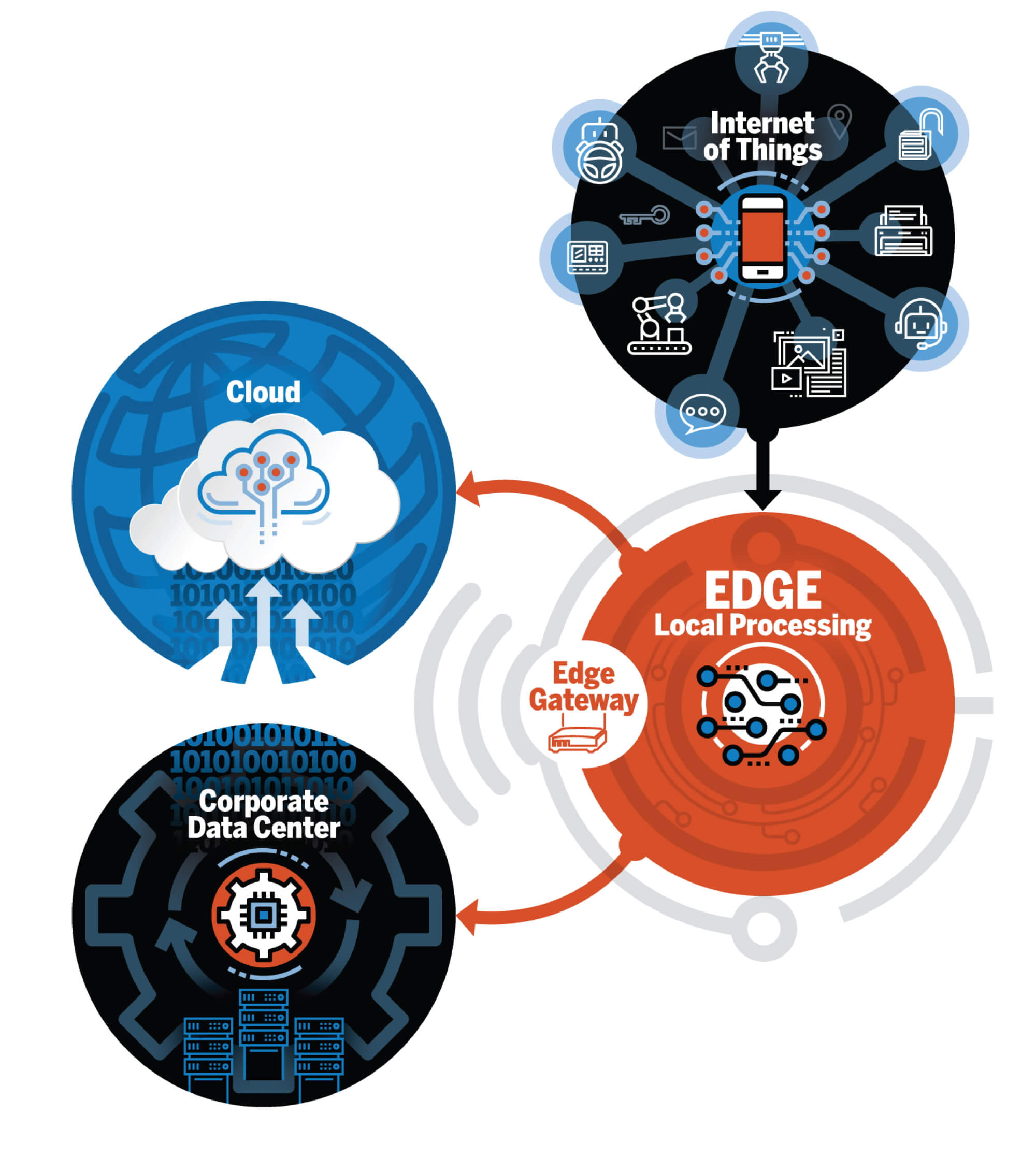
Edge computing can be explained as the technology to “bring the cloud to you – the source of data at the edge of the cloud”. Just like the name, Edge computing is done at or near the source of data.
Edge computing is transforming the way data travels and be processed from billions of devices around the world. The growth of IoT devices and new applications that require real-time computing power continue to drive the edge-computing technology.

Why Edge?
The first bonus to edge computing is the speed of data travel.
Imagine having to travel across the world to access your data if your cloud server is far away. The speed of data traveling is usually seen as “ping”, and the higher “ping” you have, the longer it takes for data to travel.
This is called as the “lag” in connection. And for some businesses, a fraction of a second can cost them more than expected, for example, in the healthcare industry or self-driving cars.
This is why edge computing is used to reduce latency and speed up the process.
Another major advantage about edge computing is the decrease of information leakage and security threats. One of the most main concerns regarding cloud computing is the risk of distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks and power outages.
Edge computing distributes processing, storage, and applications across a wide range of devices and data centers, which makes it difficult for any single disruption to take down the network.
Furthermore, IoT edge computing devices will continue to operate effectively on their own even through disconnections because they handle vital processing functions natively.
Yet, we cannot deny that security for edge computing devices might pose as a threat as edge computing devices are not as secured as data centers from large companies. This can be solved by making sure these systems are protected at all time and the data is encrypted, and that the correct access-control methods and VPN tunneling are utilized.
The increase of IoT devices also produces a massive amount of data to be computed at data centers, pushing network bandwidth requirements to the limit. Edge computing also reduces the costs of bandwidth for data travelling since instead of going the long distance, devices are connected to closer servers, which aids in controlling the bandwidth.
For instance, instead of uploading everything onto the cloud at once, the data is saved and processed at the edge, then only the important data gets transferred to the cloud database. This successfully saves your internet pipes. Especially with the birth of 5G, edge computing infrastructure can be supported even more.

Edge Computing Applications
Autonomous Vehicles:
Say hi to self-driven cars. Without edge computing technology, this would have not been possible for many more years.
Tesla successfully introduced their line of self-driven car based on the use of edge computing systems, which involves reducing bandwidth and handling instructions and directions in real time through sensory data and autonomous AI systems.
Healthcare Devices:
In order to have the fastest reaction time, healthcare devices are now equipped with edge computing systems to alert caregivers when help is needed. In addition, robots are assisting doctors in performing surgeries and are required to analyze data in a safe and accurate way, in a short amount of time.
Using an edge computing infrastructure can deliver centralized, automated security policies to each location and ensure unified HIPAA compliance while spread across multiple locations.
Smart Cities:
When you talk about smart cities, you think about IoT, and edge computing systems are one of the core elements of nowadays IoT.
Using edge computing systems and IoT, city gadgets can collect information to do fundamental processing tasks, and along with autonomous vehicles, the day where humans no longer need to tell machines what to do is no longer far.