Edge Computing VS Cloud Computing: Differences, Benefits, and Best Practices
Content Map
More chaptersIn 1999, Salesforce pioneered the idea of delivering enterprise applications to clients over the internet. Without leaving the office, anyone with internet access could purchase and download their software, which was hosted on a centralized data server.
Since then, the popularity and adoption of cloud computing has skyrocketed. On-demand streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and Spotify have changed the way we consume film, TV, and music. Meanwhile, companies like Tesla and Google are using the cloud to produce the first truly autonomous vehicle.
Going Beyond Cloud Computing
Yet despite these advancements, cloud computing has its limits. Poor bandwidth and latency can slow the transmission of data, creating bottlenecks and delays. Also, the need for a consistently reliable internet connection, especially in rural areas, can limit who gets to use cloud computing.
This is where edge computing comes in. By promising to fulfill the shortcomings of cloud computing, edge computing has grown in popularity. Companies like NEC are using it to develop walkthrough facial recognition systems, while New York City is using it to create sophisticated traffic management systems.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet. From software and analytics to storage, servers, databases, and intelligence, a wide range of digital services can be transmitted over the internet (the “cloud”). Cloud computing has a range of consumer and business applications, from streaming film and television shows, to storing emails and creating personalized digital marketing solutions. Cloud services are hosted at a vendor’s central data center and managed by the cloud services provider.
In essence, cloud computing lets you rent instead of buying your IT infrastructure. You no longer need to buy a physical server to store data; instead, you can store it on the internet through a cloud computing provider. Usually for a monthly fee, the provider will oversee the operations of your cloud storage service, ensuring your data is safe, secured, and accessible at all times.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Low Maintenance
Cloud hosting providers take care of the maintenance for you. This includes updates and scheduled maintenance, as well as urgent repairs when needed. Thus, you save time and hassle.
Reduced IT Costs
Since there is no physical infrastructure, the ongoing cost of cloud maintenance is low. There is no need to worry about adverse weather, theft, or natural degradation damaging your physical device. The main ongoing cost is your subscription service to the cloud provider itself, who will maintain the cloud for you.
Scalability
You can scale your cloud infrastructure to suit your changing business needs. Rather than purchasing and installing new software, cloud computing enables you to add and subtract whatever cloud-based services you need at any time.
Improved Collaboration
Cloud computing lets your team and customers collaborate with ease and efficiency. From collaborating on cloud-hosted word documents, to sharing contracts to electronically sign, the cloud lets you share files, data, and information at a rapid pace.
What is Edge Computing?
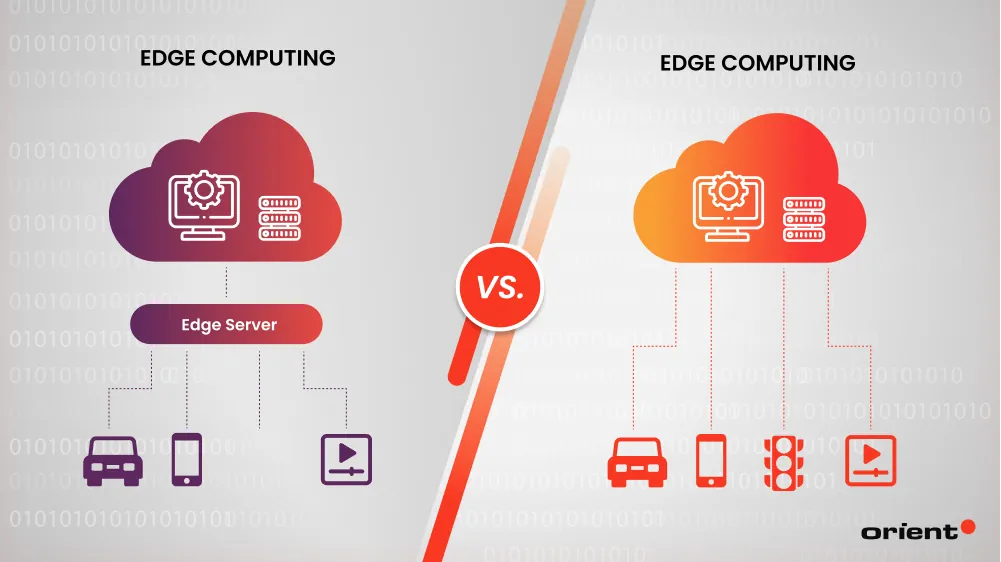
Edge computing is a distributed Information Technology (IT) architecture, where computing is done at or near the source of data. This is achieved by using physical equipment like Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, cameras, and edge nodes. These devices bring computing power to the edge of the network or device, allowing for faster data processing, reduced latency, and increased bandwidth.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Reduced Latency and Bandwidth Bottlenecks
Edge computing closes the gap between computing power and the source of data. This helps speed up the transfer of data, resulting in faster, more reliable services. The risk of bottlenecking the device is also reduced, as there are fewer data sources connecting to the one edge device.
Improved Security and Privacy
With edge computing, there is no centralized server. And, there are fewer checkpoints for the data to travel through to reach the edge device. This means there are less ways for hackers to gain unauthorized access to your sensitive data. Of course, built-in security measures, like access control and surveillance, will enhance the physical security of the edge device.
Greater Reliability
If a centralized server goes down, so does everything connected to that server. However, by allocating a portion of your computing to the edge, you are not reliant on just one server to run your IT operations.
Complements Existing Workflow
As opposed to replacing cloud computing, edge computing works with it. For example, autonomous vehicles rely on cloud computing to receive data, such as maps and traffic data. However, for more time-sensitive requests, such as whether to swerve left or right to avoid an object, edge computing can process that request in conjunction with the rest.
Differences Between Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
Edge Computing
- Ideal for collecting and processing data that is time sensitive.
- Since most edge computing is performed on physical devices, the storage capacity is limited.
- Edge devices can be secured with a variety of security measures. Encrypted tunnels, firewalls, access controls, and more. This gives businesses more control over who can access those devices and when.
- Edge computing is located at or near the source of data. Since the data does not have to travel far, this results in faster response times.
- Does your industry have specific data security and privacy laws? If so, then delegating some – or all – of your data processing to the edge can help you abide by those laws.
Cloud Computing
- While cloud computing is fast, it is not ideal for applications that require split-second decision making.
- Cloud computing offers a wide range of virtual storage solutions. But, how much you get depends on your cloud hosting plan.
- Cloud computing security consists of a set of policies, controls, procedures, and technologies to protect cloud-based systems. These measures help protect cloud data, support regulatory compliance, and protect consumer privacy.
- Most cloud computing servers are located far away from the source of data. Sometimes across multiple regions, even overseas. This leads to increased lag and latency as the data must travel further.
- Not every cloud hosting provider is equal when it comes to national and industry compliance. Some service providers may not meet the standard you request to protect sensitive consumer and business data. Therefore, do your research and compare services before you pick the right one.
Key Takeaways

Whether you invest in a cloud or edge computing solution – or both – it is important that you pick the right service for the job.
For instance, if your business relies on the fast, timely delivery of crucial data, then the speed and performance of the edge is a great choice. If, however, you need to handle large volumes of data from multiple sources, then the cloud could be for you. You may even need a combination of both.
A hybrid cloud and edge computing solution will mean different things to different organizations. As long as you pick a solution that helps you run your business more efficiently, then you’re on the right track. There are many ways to use the cloud and the edge to your advantage. So, pick what suits you best!