Augmented Reality in Healthcare: Is AR Really Transforming the Medical Industry?

Content Map
More chaptersThe gap between the digital and physical worlds has always been one we wanted to bridge. This desire is frequently portrayed in sci-fi movies, where a character layers images onto the physical world while interacting with it and making informed decisions in a matter of minutes.
At this point, you have probably paused and noticed that this technology does exist in real life - it is augmented reality or AR for short. Although AR technology is often associated with the gaming industry, it has made its way into numerous industries. Bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds allows us to fully take advantage of the rich online information. AR technologies have opened up endless possibilities.
How has augmented reality transformed the healthcare industry? This article will guide you through its marked impact both inside and outside the healthcare clinics.
Augmented Reality in Healthcare - What Do the Numbers Say?
Augmented reality has more or less seemed like a buzzword. Is it truly worth the hype? Are its capabilities really as remarkable as people say? Before we start discussing the questions, what exactly is AR?
What Is Augmented Reality?
According to Gartner, Augmented Reality (AR) involves the real-time utilization of textual, graphical, audio, and other virtual enhancements in conjunction with physical objects. AR integrates and enhances user interaction with the physical world, as opposed to a simulation.
AR (Augmented Reality) and VR (Virtual Reality) Difference

When it comes to modern technologies that involve enhancing the user’s experience in the fictional or digital world, you often hear the terms AR (augmented reality) and VR (virtual reality) go together. These terms are easily mixed up due to their many similarities.
AR and VR bear a number of distinctions, which you can read all about in our in-depth comparison article.
In short, however, the most significant difference between the two is the fact that augmented reality enhances your environment by adding digital objects to a real-world scene, often through the use of a smartphone’s camera. Pokemon Go is a great example of AR. Virtual Reality, on the other hand, is a fully immersive experience that substitutes a virtual environment for the real one. Imagine you are walking through a museum in France without having to visit the country.
Statistics
The following noteworthy AR data in the healthcare sector demonstrate that this is not just a developing technology but one that is rapidly changing and growing.
- The augmented reality Internet of Things (IoT) in hospitals is predicted to be worth 20 to 30 billion US dollars by 2025, and it is projected to increase to 40 to 90 billion U.S. dollars by 2030.
- Fortune Business Insight reports that in 2022, the augmented reality market was valued at USD 42.20 billion. By 2030, it is anticipated to reach USD 1109.71 billion.
- When it comes to technology, it is reported that surgical applications, rehabilitation training, and medical education are some of the most popular uses of augmented reality.
AR Application in Healthcare
The implementation of AR technology in healthcare offers a range of advantages, including improved access to essential healthcare that would otherwise be difficult to obtain, the reduction of pre-operative anxiety, the reduction of invasive procedures, the acceleration of diagnoses, and the list goes on.
Due to its advantages, it has been utilized in different areas of the medical field.
AR Surgery
AR headsets aren’t meant solely for gaming purposes, although this is often the very first use people will think of. Surgeons use AR headsets for guidance during their operations.
Complex surgeries require a high level of precision. Surgeons are quite literally holding human lives in their hands, so every move matters. With AR, medical practitioners have the overlayed image of the human anatomy in front of them - which they can refer to when needed without being distracted from the actual task at hand. Surgeons can refer to the patient’s 3D model of their organs or tumors, too.
AR allows doctors to process a large amount of data in a relatively short time with the help of other technologies, like artificial intelligence (AI). As a result, surgeons are able to perform the surgery with more precision and avoid causing damage to other organs or blood vessels.
Recently, Dr. Cezar Mizrahi at the emergency department of Jerusalem’s Shaare Zedek Medical Center (SZMC) used augmented reality and a surgical robot to carry out incredibly complex spinal surgery on a 25-year-old patient.
Medical Training
Everyone knows medical training is a long and intense journey. The traditional method, where lectures and memorization have been emphasized, has stayed effective for decades. However, AR technology provides medical students and lecturers with a novel approach to medical training.
First, the most basic function of AR - superimposing digital information onto real-world objects to create a 3D experience to interact with both the physical and digital worlds. Medical students can use AR to explore human anatomy. With a mobile device and the right AR software, students can visualize the internal human body structures by pointing the camera toward a model or even a real human.
In addition, augmented reality applications are an effective tool for surgical simulation. In addition to providing students with visual aids such as arrows or labels to illustrate anatomical structures associated with surgery, augmented reality technology also facilitates the practice of surgical technology. With virtual objects and AR software, students are learning how to deal with complications and situations during surgery. Because everything is carried on in an AR environment, the process can be shared with one another as long as students are wearing their AR glasses.
Pain Management
Hospitals and healthcare facilities are often associated with pain and fear. With the help of AR and VR, the pain and fear can be relieved by immersing patients in therapeutic environments. This virtual environment is controlled by healthcare professionals to make it easier for patients to relax and cope with pain.
With the same use in mind, AR is extremely beneficial when it comes to physical therapy. Physical rehabilitation is hard and takes up long periods of time. In the virtual environment, patients can work on their rehabilitation in a safe environment with the most comfort. Advanced technologies, like artificial intelligence - AI - and machine learning, can help customize the pain management experience.
A recent Cleveland Clinic trial has found that an AR headset is an effective tool to help Parkinson’s patients with their Gait Functions. To be specific, a digital avatar will give the patient instructions while also tracking their movements and responses. This data is collected so physicians can create and improve their future sessions. The clinical trial has produced positive results.
Telehealth
The word “telehealth” refers to a broad range of telecommunications technologies and strategies used to deliver healthcare remotely. Telehealth has become extremely popular during the pandemic. However, the future of telehealth goes beyond the pandemic.
Patients with impairments or the elderly no longer need to be present at a healthcare institution equipped with a plethora of expensive medical devices. Augmented reality technology enhances the telehealth experience - doctors have vital patient records overlayed to examine and provide quick feedback. If patients have difficulty describing their symptoms, AR devices help patients visualize different conditions and compare those with their own. This is also a great way to help educate patients about their conditions and treatments.
All in all, AR, alongside other technologies like AI and the Internet of Things (IoT), takes telehealth to another level, where patients have a lot more access to medical care and professionals. AR surgery, medical training, pain management, and telehealth are only some of augmented reality’s applications in healthcare. It is also a great tool to assist in the treatment of mental health (e.g., post-traumatic stress disorder), nurses’ training, medical device and troubleshooting, telemedicine advancements, and so on.
Challenges of Using AR in the Medical Field
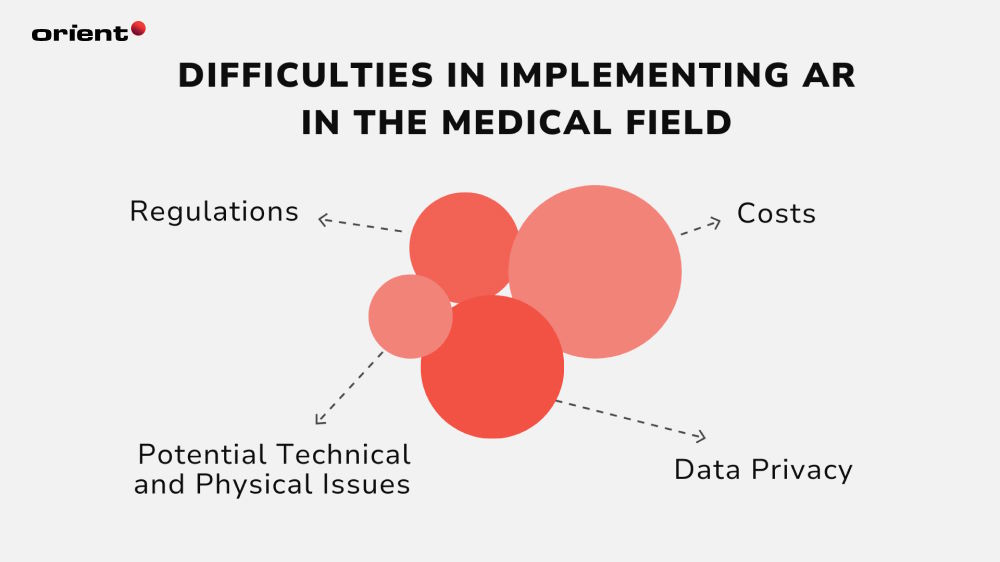
Despite being a technological innovation, AR technology is still in its infancy and comes with its challenges.
Costs
It is impossible to talk about AR without its devices: the head-mounted display, the app, and the software that is often paired with it. Despite the good intentions of AR technology, where the ultimate goal is to make healthcare services accessible for everyone, the high costs that come with it might be one of the largest hindrances. The costs might stop smaller healthcare providers from adopting the technology.
Additionally, tech companies developing AR headsets and AR apps are having difficulty expanding their reach due to a lack of funding.
Potential Technical and Physical Issues
Healthcare clinics are still hesitant to adopt AR in their daily practice. Part of this is due to the technology’s infancy, but it is also due to the limits of the existing computers in the hospitals. The content and images provided by AR might also run into problems like errors in displaying the depth or position of the anatomy, low-contrast images, etc.
The technology might also cause negative physical issues for doctors and nurses. They might experience neck pain, visual effects, or information overload.
Regulations
The usage of AR devices and apps must adhere to a comprehensive set of regulations, rules, and insurance regulations. Additionally, the ethical considerations of patient privacy and informed consent should be taken into account.
Data Privacy
Like any other kind of technology, AR poses the risk of cyber-attacks. The large amount of sensitive data collected makes AR devices and software a prime target for hackers. This can be prevented, however, with a proper security management system.
AR Is Already Transforming Healthcare

Although augmented reality (AR) technology has yet to reach its full potential, it has already initiated a number of positive changes in the healthcare sector. AR has consistently demonstrated its potential to be a cutting-edge technology, both within and outside the hospital, making the medical profession more efficient and the patient experience less intimidating.
Are you equally enthusiastic about the future that AR technology can bring to the healthcare industry and beyond? Do you want to know what your choices are when it comes to AR technology? Contact Orient Software today, and we will be happy to help!