Framework Finesse: COBIT Vs. ITIL in the Digital Arena
Content Map
More chaptersITSM (IT service management) is the process of organizing, coordinating, supervising, and enhancing information technology services to fulfill user requirements and assist businesses in accomplishing their objectives.
An ITSM framework involves processes and practices to manage IT services, spanning network infrastructure, applications, and business services. It operates vendor-independently, allowing seamless integration across diverse IT environments.
Two recognized IT governance and management frameworks are ITIL and COBIT. In this article, we will take a closer look at COBIT vs. ITIL and try to understand their key components, approaches, principles, and key differences. You will have a better idea of how to implement ITSM, as 90% of the 451 global companies that were surveyed in this paper did.
A Brief Overview of COBIT & ITIL
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
ITIL is a globally recognized ITSM framework designed to efficiently manage IT services within organizations that are short on the Information Technology Infrastructure Library. Developed initially by the UK Government in the 1980s and now administered by AXELOS, ITIL offers a comprehensive set of best practices, processes, and procedures across the entire lifecycle of IT services.
With guidelines for efficient service management from the IT department’s perspective, ITIL aims to:
- Support daily process organization and routine management
- Maintain high service quality
- Maintain excellent operation
- Enhance customer satisfaction
It is one of the most popular frameworks for IT service management. Its latest iteration was released in 2019, called ITIL 4.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information & Related Technologies)
COBIT is the acronym for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is a comprehensive framework developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) in the mid-1990s to address IT governance and management challenges. Initially focused on financial auditing, it has since expanded to encompass broader governance activities, emphasizing IT governance for business success.
COBIT acts as a bridge between IT and business goals. It offers a high-level roadmap for:
- Developing and managing IT governance practices
- Facilitation for increased value
- Reducing and maintaining privacy standards
- Risk management
Businesses use COBIT for maturity models and metrics to measure their business objectives, process coordination, and success. Its latest version is COBIT 2019.
Key Components & Principles

COBIT
Framework
COBIT is made to be compatible with other frameworks and standards like ITIL and ISO 27001. This component is great for linking business demands while also putting in place IT governance goals and the best management processes.
Process Descriptions
COBIT is a framework laser-focused on processes. It can be considered the common language for teams in the same organizations, drawing out the essential processes and activities, like planning, running, monitoring, and improvement plans.
Control Objectives
This framework sets a list of control objectives, or in other words, a list of requirements that help run the processes smoothly, manage risk effectively, and comply with regulations.
Maturity Models
COBIT offers maturity models to closely examine the processes’ potential and maturity, address gaps, and then offer a roadmap for improvement.
Management Guidelines
You have probably noticed by now that COBIT is a framework that highlights improvement. Management guidelines encourage enterprises to regularly conduct assessments, measure performance, and make sure that the existing processes align with the business goals.
ITIL
Service Strategy
This component understands both the company’s goals and customer’s needs. It involves the IT Service Delivery model, ensuring that it aligns with the organization’s demands while setting processes to monitor and update configuration items.
Service Design
ITIL continuously works on planning and examining the delivery of business objectives through the lenses of IT process and service processes.
Service Transition
With proper planning and change management, the framework identifies and reduces risk. ITIL helps replace outdated IT services with modern ones.
Service Operation
Not only does ITIL manage and plan, but it also provides regular support through resources like backups and service desks. This is to ensure smooth daily operations.
Continual Service Improvement
All the planning, management, and continuous support is to finetune the IT services. The framework helps identify any bottlenecks and establish KPIs and other performance analyses for further enhancement.
Objective and Approach

COBIT
Objective
The main goal of COBIT is to:
- Control and set the right direction for enterprise IT
- Align business goals with IT goals
- Bring IT value to business
- Manage resources, risks, and efficiency effectively.
Approach to IT
- Top-down, more focused on the IT side
- A clear distinction between management and governance in IT
ITIL
Objective
The main goal of ITIL is to:
- Looking for opportunities for continuous operational perfection. This means reducing the cost while maintaining efficiency.
- Organizing IT services and IT service management processes - more specifically, the IT department’s tasks like design, transition, operate, and improve services.
Approach to IT
- Bottom-up, mostly from the IT side
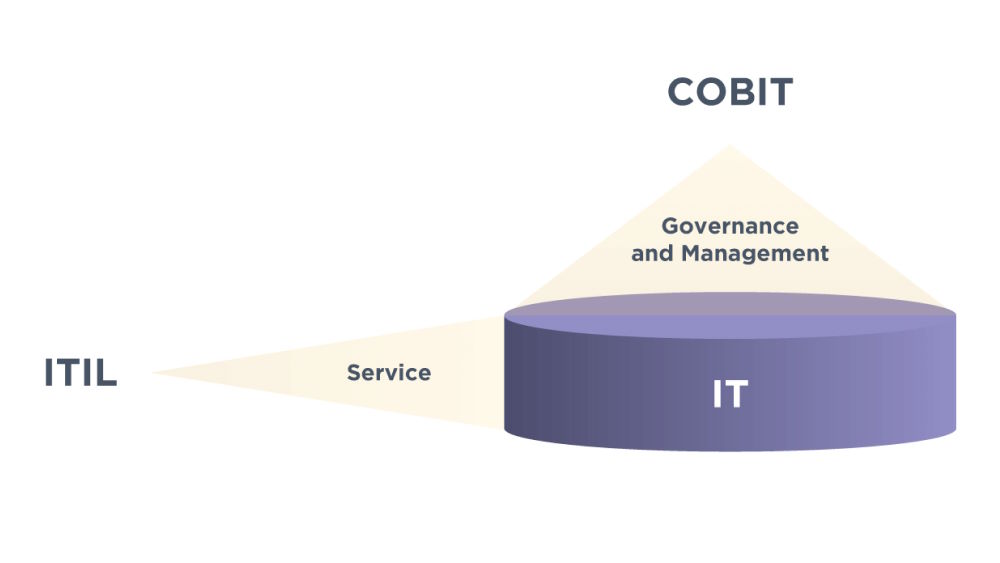
- ITIL doesn’t clearly distinguish between management and governance. Therefore, from COBIT’s point of view, ITIL mostly handles management, and COBIT deals with governance.
Principles
COBIT
COBIT focuses on four main areas: management, security, risk, and governance. COBIT is built upon five core principles essential for effective information security management and governance.
1. Meeting Stakeholder Needs
COBIT ensures organizations meet stakeholder needs without compromising data security.
2. Taking a Holistic Approach to Governance
COBIT emphasizes enterprise end-to-end governance involving IT, auditing, and management, utilizing enablers across principles, structures, information, processes, and employees.
3. Covering the Entire Project
COBIT combines enterprise governance with IT to guarantee thorough coverage of all business operations and procedures connected to data/information flow and technology. This includes generating value, leveraging enablers efficiently, allocating roles and duties, and thoroughly specifying project scope to guarantee that governance and value creation are applied throughout the entire company.
4. Single Integrated Framework
COBIT provides a unified framework to manage technological changes and risks and govern information consistently throughout the firm, though customizable at times to meet the organization’s needs.
5. Creating a Difference Between Governance and Management
This is a principle that enterprises might struggle with, but it is necessary to clearly define responsibilities. COBIT uses different frameworks for governance and management.
For governance, the EDM (Evaluate, Direct, Monitor) method is used. This means governance is focused on making decisions, outlining objectives, and monitoring performance.
For management, it adopts the PBRM (Plan, Build, Run, Monitor) method. This means management is focused on carrying out decisions.
ITIL
ITIL 4 is made up of 7 guiding principles. Not only do these concepts help adapt ITIL 4 effectively, but they also help guide organizations through all circumstances.
1. Focus on Value
ITIL ensures that all organizational efforts contribute directly or indirectly to stakeholder value. In this context, value entails both intangible (such as customer experience) and tangible (such as financial) aspects.
2. Start Where You Are
ITIL leverages existing resources and capabilities rather than starting from scratch. This principle adopts the Lean-Agile mindset and sets a realistic approach toward value delivery mechanisms and current architecture.
3. Progress Iteratively with Feedback
ITIL breaks down initiatives into manageable sections and incorporates feedback throughout the process. It is easier to obtain stakeholder confirmation and collect data in smaller steps. Data helps build trust and improve services effectively.
4. Collaborate and Promote Visibility
ITIL fosters collaboration across boundaries and promotes transparency to achieve long-term success. After all, collaboration extends to customers, users, suppliers, and all organizational stakeholders and ensures consistency through a common knowledge base.
5. Think and Work Holistically
ITIL recognizes that no service or component exists in isolation and ensures integration across all aspects of service delivery. Effective management highlights integrating technology, rules, organizational principles, and procedures.
6. Keep it Simple and Practical
ITIL eliminates unnecessary steps and focuses on practical solutions that deliver value. This benefits DevOps and Agile professionals who already adopted such a mindset. Simplifying workflow and regulations allows for the information to flow easily into the decision-making process.
7. Optimize and Automate
ITIL utilizes resources efficiently and leverages technology to streamline processes wherever possible. ITIL focuses on improving and perfecting operations; this principle lays out a guide to enhance value delivery, quality, and customer experience.
Key Differences between COBIT & ITIL
To wrap up this article, here is a table that provides a broad overview of COBIT and ITIL’s differences.
| COBIT | ITIL | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Establishes guidelines for senior management to help them understand how to handle enterprise IT. | A roadmap outlining the steps required to arrange the everyday work of IT staff members. |
| Purpose through a question | “What is the best way to utilize the resources of my IT department to benefit the company?” | “How can I most effectively manage the workload of my IT teams?” |
| Scope | Broader than ITIL since it focuses on the entire organization | Stays focused on the IT domain. |
| Approach | Top-down approach, emphasizing IT service governance. | Bottom-up approach, from the IT perspective. |
| Structure | Organized around domains and processes, with a focus on control objectives and management practices to achieve desired outcomes. | Organized around the IT service lifecycle, with guidance provided for each stage of the lifecycle, including service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement. |
| Components | - Framework - Process descriptions - Control objectives - Maturity models - Management guidelines | - Service strategy - Service design - Service transition - Service operation - Continual service improvement |
| Principles | 5 core principles: - Meeting Stakeholder Needs - Taking a Holistic Approach to Governance - Covering the Entire Project - Single Integrated Framework. - Creating a Difference Between Governance and Management | 7 key principles: - Focus on value - Start where you are - Progress iteratively with feedback - Collaborate and promote visibility - Think and work holistically - Keep it simple and practical - Optimize and automate |
| Certificates | - COBIT 2019 Foundation Exam - COBIT 2019 Design and Implementation Exam - COBIT Bridge Workshop | - ITIL Foundation Exam - ITIL Strategic Leader (SL) Exam - ITIL Managing Professional (MP) Exam |
Which ITSM Is Right for You? Can You Use Both COBIT & ITIL?
COBIT will be more suitable for you if:
- IT governance, risk management, and compliance are priorities for your company.
- You operate in an industry with strict standards and regulations, e.g., finance.
- Instead of only service management, you would rather have a framework that covers a wide range of IT-related tasks.
ITIL is right for your organization when:
- You are laser-focused on improving IT service management.
- You need an actionable roadmap to guide you on how to improve IT services and processes.
- You wish to improve your IT staff’s competencies within the framework of service management.
However, there is no problem in using both COBIT and ITIL. As a matter of fact, many organizations have been using both to operate their organizations effectively.
So, should your business use both COBIT and ITIL? Well, it depends. The choice really hinges on your organization’s goals and priorities. For many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), COBIT and ITIL are seen as two separate but valuable tools.
Still unsure? Don’t worry. Let Orient Software lend a hand. Our experts are ready to chat and get to know your organization better. Together, we’ll figure out the best IT service management approach for you. Reach out to us today, and let’s make IT work for you!