There’s this saying, “Blueprint no matter what you build”. No one would want to hire a team of construction workers who do foundation laying, structural framing, or installing utilities blindly.
The same can be said for mobile app development. The development process is often long and complex, and without clear instructions and planning, it’s impossible to produce a final product that works well and meets all the requirements.
Today’s article explains the 9 crucial stages of a mobile app development cycle, all the tools and tech you need to optimize the process, and challenges that you might encounter along the way. Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- The mobile app development cycle consists of 9 steps: researching, wireframing, technical feasibility, designing UX/ UI, prototyping development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
- Mobile app development can be a long and complex process; that’s why it’s essential to have the right tools and software in your bag.
- AI, ML, cloud-native architectures, microservices, and IoT are some of the technologies that mobile app dev teams need to watch out for.
- Creating mobile applications comes with its own set of challenges. The key to solving them is to keep a user-centric approach, applying the best practices from day one, and planning every step carefully.
9 Critical Stages of the Mobile App Development Lifecycle
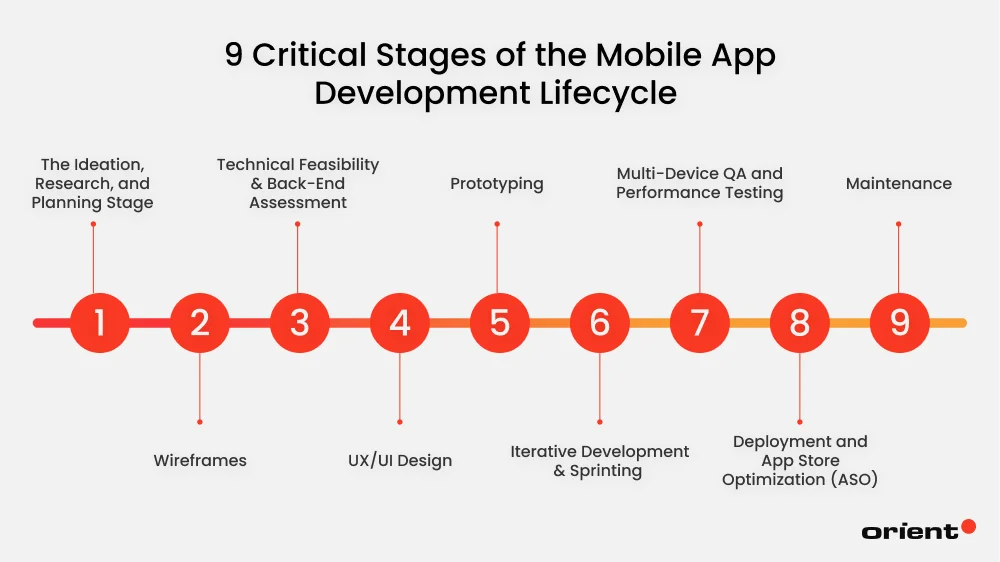
Step 1. The Ideation, Research, and Planning Stage

Prior to hitting the codebase, there is a lot of groundwork to cover. One of the biggest mistakes a team can make is rushing into production without spending adequate time on the conceptual groundwork. Here are some questions that you need to have answers to, and these answers should be as detailed as possible.
- What is the purpose of your app? In other words, what pain point does your app address?
- Is there a market demand for the app? What does market research tell you?
- Who is the target audience?
- What is your preferred platform (iOS or Android, for example)?
- Who are your competitors? How does your app and its features differ from theirs?
- What is the estimated development timeline?
- What is the budget for the project?
Document these answers. While they act as a guide during the project, it’s also necessary to refine them as you go.
Step 2. Wireframes

After the initial discovery and research phase, it’s time to lay down the very first sketches. Wireframes serve as the architectural blueprint. They are a low-fidelity, basic layout of an application’s user interface that prioritizes functionality (such as button placement and navigation flow) over visual design (colors, fonts, and graphics). Wireframes allow developers and stakeholders to take a critical look at the app’s structure without the distraction from visual aspects.
Step 3. Technical Feasibility & Back-End Assessment
After nailing down the requirements and the basic structure of the app, it’s time to approach the project from a technical aspect.

Here are the core factors one needs to carefully assess to make sure the tech can support the app’s functionalities.
- Platform (Android, iOS, or cross-platform)
- Backend architecture and tech stack
- APIs and third-party integrations
- Data diagrams and data integrations
- Push-notifications
- Non-functional specifications like performance, security, and scalability
By the end of this stage, you might find that some initial features aren’t possible. Don’t worry. Return to the drawing board and review the design. By the end of the review, your team will have a clearer picture of specific features, a tech document listing system architecture, data models, and user journey flow. Team members will also have a better idea of the limits regarding timeline, budget, and tech.
Step 4. UX/UI Design
After finalizing the app’s structure, the following step is to make it visually appealing and user-friendly.
UI (user interface) design involves all the elements that you can see and interact with on the screen: menu buttons, graphics, animations, micronations, and more. A good UI design is simple and consistent.

A UX (user experience) focuses on creating intuitive interfaces for handheld and wearable devices. Because these products are used on the move, designers prioritize accessibility, clarity, and efficiency to ensure quick, frictionless interactions in real-world contexts. It incorporates usability, design, branding, and function.
All in all, a strong UX/ UI mobile design is simple, intuitive, and user-centric.
Step 5. Prototyping
Prototypes are bridges that connect the gap between concept and reality. Prototyping involves developing an early version of a mobile app to illustrate its layout, user flow, and core functionality. It gives the team a tangible way to see how users will interact with the application before the actual development begins.
They aren’t real apps but are designed to feel like one. Prototypes are designed to be interactive models that mirror the final product’s look and feel, allowing the team to catch design flaws early without costly reworks.
Step 6. Iterative Development & Sprinting

After extensive planning, it’s time for the development stage, which often takes the most time in the whole development cycle. To turn every line of requirement or design elements into functional lines of code, the main components of this stage involve the following.
- Frontend development: The frontend is everything that users see and interact with. The goal of frontend development is to provide a seamless, high-performance interface that translates user taps into actions using technology like Swift (for iOS), Kotlin (for Android), or React Native/Flutter (for cross-platform development).
- Backend development: Backend is everything that users can’t see, but the “brain” of the entire app. This is where all the heavy lifting is happening to manage user accounts, process payments, and store information securely. Typical tech involved is Node.js, Python, or Go.
- API integration: Application Programming Interface, or API, is the bridge that connects the front and backend and allows them to talk to each other. API’s main goal is to ensure data flows instantly and accurately between the user’s device and the server.
The CI/ CD pipeline, security and data privacy, third-party integrations, and performance optimization are other things that a developer must handle during this phase. Most modern teams follow the Agile work method, where a large project is broken down into smaller cycles (called sprints). The team presents each small piece to the client and integrates their feedback before moving on to the next cycle.
Step 7. Multi-Device QA and Performance Testing

Once the development starts, the app needs to go through rigorous testing to make sure clients receive an app that functions seamlessly with as few bugs as possible. The most basic tests involved in this stage include:
- Functional testing (Does it work?): Ensures every feature behaves as defined in the requirements, from individual code units to full system integrations, and confirms that new updates will not break existing functionality.
- Usability testing (Is it easy to use?): Evaluates whether real users can navigate the app intuitively and complete key tasks without confusion.
- Compatibility & device testing (Does it work everywhere?): Verifies that the app runs consistently across different devices, screen sizes, OS versions, and orientations despite mobile platform fragmentation.
- Performance & load testing (Is it fast?): Assesses how quickly and reliably the app performs under various conditions, including high traffic, slow networks, and limited device resources.
- Security testing (Is it safe?): Confirms that user data, authentication, and transactions are properly protected and comply with security and regulatory requirements.
By implementing a mix of automated testing and manual testing, the team can ensure a successful app launch in the future.
Step 8. Deployment and App Store Optimization (ASO)
It is finally time for deployment. To ensure a successful launch, there are several things to keep in mind and finalize, as app stores often have rather strict rules.
- Preparing the app: Developers set up store listings, including the app description, screenshots, icons, and other assets, ensuring everything complies with Apple App Store and Google Play guidelines.
- Submission process: The app is uploaded to the relevant app stores through developer accounts. Each platform runs its own review process to check for bugs, policy violations, and technical issues. Reviews can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks.
- Review and revisions: If the app is rejected, developers address the issues flagged by reviewers and resubmit until approval is granted.
- Beta testing (optional): Some platforms allow a beta release to a limited group of users, helping teams collect real-world feedback and make final refinements before launch.
- Launch: Once approved, the app is published and made available for end-users to download from the app store.
To help the app rank higher in store searches, it’s a great idea to do app store optimization. It starts with keyword research to understand demand and competition, then applies those insights to your app title, metadata, description, and category selection. This increased visibility drives higher conversion rates, user retention, and organic installs.
Step 9. Maintenance
The lifecycle doesn’t end at product launch. When users start using the app, it’s important to monitor its performance, feedback, and performance metrics. This allows the team to make timely improvements and show the users that the team cares about constantly bettering the app.

To stay relevant, here are the basic tasks every team needs to do:
- Bug fixes: Resolving issues reported by users to maintain a smooth experience.
- Updates: Introducing new features or refining existing ones based on user feedback and usage patterns.
- Compatibility: Keeping the app aligned with new devices and operating system updates to ensure consistent performance.
Not only does maintenance keep your clients happy, but it also keeps the app stable and highly competitive.
Mobile Development Technologies to Watch in 2026

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are moving from “nice to have” to built-in parts of how apps are designed, built, and maintained. Developers will make use of AI in a variety of tasks, including natural language features, code generation, and automating repetitive work. AI-driven experiences will become common, like chatbots or smart recommendations.
Low-code and No-code Platforms
Low-code and no-code tools will continue lowering the barrier to app development. With drag-and-drop interfaces and prebuilt components, non-developers and small teams can launch functional apps faster without heavy engineering investment.
DevOps and DevSecOps
Modern DevOps is moving toward cloud-native development, microservices, and automation. Rigid monolithic systems and manual processes are being replaced by modular, scalable architectures designed for continuous delivery. At the same time, DevSecOps is becoming the norm, with security built into every stage of the development lifecycle instead of being added after release.
IoT Apps
IoT-driven apps continue to expand across industries, from wearables and smart devices to industrial systems. As edge computing matures, more apps will process data closer to its source, enabling faster responses and real-time insights. The focus will shift toward building IoT apps that are not only powerful but also secure and scalable.
PWAs
Progressive Web Apps, or PWAs, will keep growing as organizations look to reach both iOS and Android users without maintaining separate codebases. With offline access, push notifications, and near-native performance, PWAs offer a practical middle ground between web and mobile.
Tools You Need to Manage the Mobile App Development Cycle Effectively

The mobile app development process is often a complex one with collaboration from multiple teams. You can keep track of the process by using manual spreadsheets, but this method is often error-prone and sometimes even creates data silos.
To combat this problem, it’s wise to use the right tools to track the process and related project issues. These tools are effective and will save you hours or costly reworks.
Project Management Platforms
Strong project management platforms save your team time, organize tasks and workflow effectively to boost productivity, collaboration, and accountability. The top tools we would suggest for this are Trello, Asana, and Jira. Wrike and Monday.com are also great choices.
Version Control Systems
As its name suggests, version control tools track and manage changes to files, such as source code, over time. They boost collaboration by maintaining a complete change history, making it easy to review edits and roll back to earlier versions if needed.
Well-known systems are Git, Apache Subversion (SVN), and Mercurial. Hosting platforms like GitLab, GitHub, and Bitbucket are also popular.
Collaboration Tools
Efficient collaboration tools in a mobile application development project are more than messaging apps. They also support feedback systems, code collaboration, and allow the team to stay in sync.
- Slack and Microsoft Teams provide a channel-based messaging platform for real-time communication.
- Zoom and Google Meet are essential for video conferencing and online meetings.
- Confluence and Notion: These are popular for creating and managing project documentation, wikis, and technical specifications.
Issue Tracking Systems
A strong issue tracker gives teams a single, reliable place to manage requests, track ownership, and understand context. By centralizing communication and using automation to route tickets efficiently, it reduces confusion and speeds up resolution.
Service Now, Jira Service Management, GitHub issues, and Linear are some tools that we suggest obtaining visibility and preventing bottlenecks.
AI-Assisted Coding (e.g., GitHub Copilot, Cursor)
AI has been evolving rapidly. More than generating texts and images, AI, in tandem with other technologies, has been widely implemented in multiple sectors, and software development is no exception. AI tools can assist developers in writing, debugging, and generating code. AI is also a great tool when it comes to error detection and automated reviews.
Popular AI tools are GitHub Copilot, Amazon Q Developer, Cursor, and Lovable.
Common Challenges in Mobile App Development and How to Solve Them
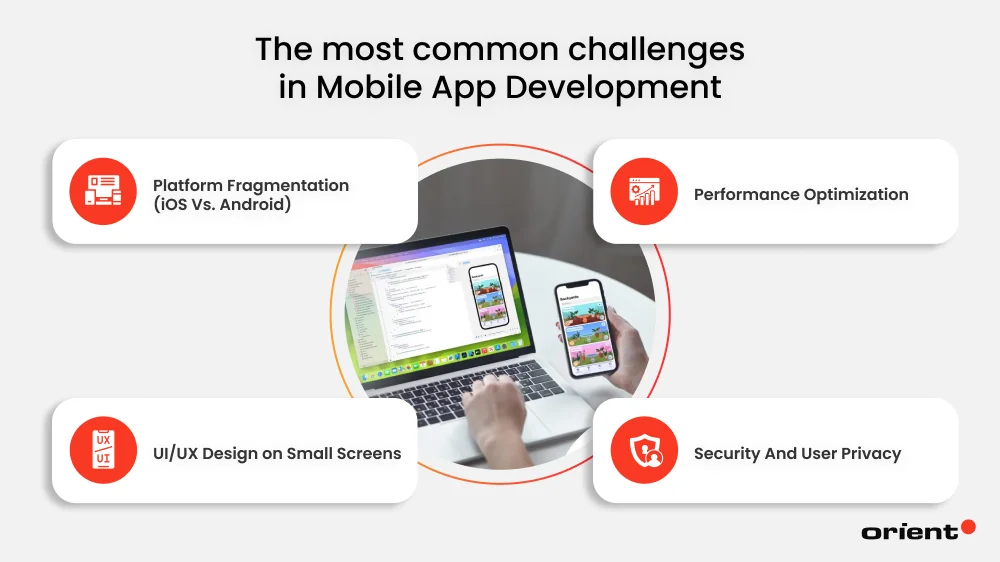
Being equipped with essential knowledge of the mobile app development phases doesn’t mean you can completely avoid common obstacles along the way. Being aware of the possible problems allows one to be better prepared and minimize risks.
Platform Fragmentation (iOS Vs. Android)
It seems that it is every developer’s dream to build a mobile app once, but be able to run it anywhere. Unfortunately, reality doesn’t allow this. Creating a mobile app for iOS platforms requires Swift, Android requires Kotlin, and cross-platform development calls for a team adept in React Native.
Working on separate native app projects doubles the time, the costs, and even the human resources. This is not to mention the challenge of ensuring the app works reliably across a broad range of devices, screen sizes, and OS versions.
The solution: Professional teams manage fragmentation through a mix of smart prioritization, flexible design, and targeted testing.
They rely on real user data to prioritize the most common devices and OS versions, set a minimum supported OS to reduce complexity, and use responsive, constraint-based layouts with scalable assets to adapt to different screens. Testing combines emulators, cloud-based device farms, and beta programs to catch issues early and in real-world conditions.
Performance Optimization
Did you know that 60% of Gen Z users expressly refuse to use an app or website if it loads too slowly, according to recent statistics from 2025? Or the fact that the likelihood of a bounce increases by 32% as the site load time climbs from 1 to 3 seconds?
It doesn’t matter how stunning your app looks, or the experiences that it promises to deliver – an app that’s crashing, taking too long to load, or has a glitchy overall experience will cause a customer to quit using it.
The solution: This issue can be countered with careful and smart coding. High-performing apps are built with performance in mind from the start, not patched together later. In other words, the team needs to apply efficient coding practices from the very beginning, like smart chasing or lazy loading, to keep the app fast and responsive.
UI/UX Design on Small Screens
Mobile apps come in all sizes: tablets, mobile phones, and smart watches. Creating a user-friendly and intuitive user experience on these screen sizes can be challenging, as developers need to ensure the functionality and fluidity. A strong UI/ UX design is one that users feel so natural, they can carry out their intended action quickly with minimal friction. Too focused on the technical aspect – as perfect as the app may be technically, users will still refuse to stick with the app.
The solution: Put yourself in the users’ shoes. What would you expect from a mobile UX/UI design? Familiar mobile patterns, clear navigation, and progressive closure all guide users naturally without overwhelming them. One way to make sure of this is regular usability testing. In short, rather than maximizing features, a great UI/ UX makes the users’ goals easy to achieve.
Security And User Privacy
- More than 75% of apps released in 2024 contained at least one vulnerability.
- In 2025, the average cost of a single data breach worldwide was $4.44 million.
These are only two notable statistics, among many, regarding mobile app security. Mobile phones have become an essential part of our everyday life, as they can provide users with entertainment, an e-wallet, and a small working device, all in one. While users are becoming more dependent on it, they are also becoming much more aware of the security risks (silent data tracking, AI-powered scams). Developers need to step up their game to gain trust from users.
The solution: Security should be built in from day one. Having a proactive and layered approach is how teams avoid data breaches and protect users’ data. It’s a good idea to follow established security standards, like OWASP Mobile Security. In short, when you treat security like a foundation rather than a feature, you’ll build the right foundation for teams to respond faster to threats and protect users.
Wrapping Up

Building a high-performing mobile app requires thorough planning, the right set of tools, and plenty of trial-and-error. It can be a long and frustrating journey, but the reward will always be worth it.
And remember, you don’t need to figure out everything alone. Why not reach out for a team of professionals, like Orient Software, to gain in-depth industry insights and have a team of professionals take care of all the common challenges you might encounter along the way? Contact Orient Software today!






















