Having a well-received mobile application is just the beginning of the entire journey. What ultimately determines its success in the long run is how it is updated and maintained over time.
In a world where Apple App Store and Google Play put millions of alternatives only a few clicks away and switching costs are effectively zero, app users are becoming more distracted than ever before. They are less patient and not willing to tolerate an app with bugs or glitches. They will not think twice about uninstalling an app and replacing it with another if the experience is not as expected.

That harsher reality raises the bar for every app owner. In a crowded market, app developers not only have to compete with a vast ocean of competitors to keep users engaged but also earn their loyalty. Once again, the way to do it is through well-run, ongoing maintenance. This article breaks a mobile app maintenance plan into a set of crucial, actionable steps. Work through the checklist and make sure you tick every box.
Key Takeaways:
Mobile app maintenance is non-negotiable. Here are a few crucial steps to a well-maintained app:
- Know the five maintenance types: Adaptive, corrective, preventive, perfective, and emergency maintenance. Each serves distinct purposes around app maintenance.
- Estimate a realistic budget. Expect the annual mobile app maintenance cost accounts for around 15% - 20% of the initial development cost, adjusting upward for frequent updates, third-party dependencies, or strict security/compliance requirements. Pay attention to key cost drivers, including complexity, technology stack, team location, update cadence, dependencies, and security needs all influence your spending.
- Follow best practices: Build a structured maintenance plan, monitor continuously, prioritize security, collect user feedback, set a predictable update schedule, and communicate transparently with users.
- Outsourcing is an option. When resources are stretched or specialized expertise is needed, outsourcing part or all of maintenance can extend your team’s capabilities without sacrificing quality.
Understanding Mobile App Maintenance Types
First and foremost, you need to understand that a living system like a mobile app requires regular maintenance and updates - those come in distinct types, not a single catch-all. Know each mode down to its core tells you how to prioritize, how fast to move, and what a well-maintained app looks like.
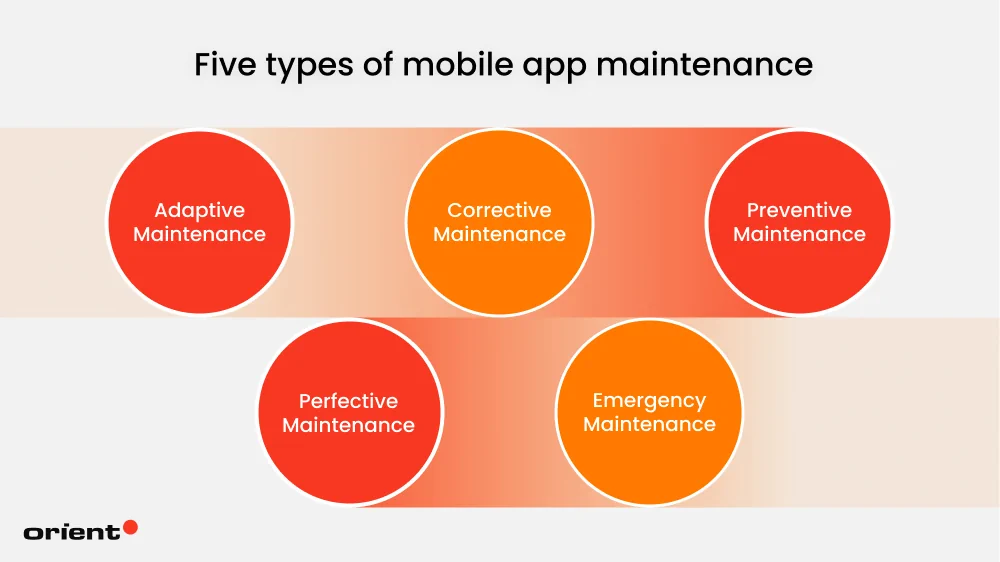
Adaptive Maintenance

This type of maintenance work is driven by external conditions that fluctuate around the mobile app, specifically new operating system versions, SDK deprecations, store policy shifts, new device classes. It does not target existing bugs or user experience issues but future-proofs the app compatibility and ensures continuous operations within an evolving technical, legal, or business environment.
Corrective Maintenance

As the name suggests, corrective maintenance refers to the systematic identification, diagnosis, and rectification of defects or malfunctions that appear in a post-released mobile application. In simpler words, it is about identifying and fixing bugs. These issues might arise from coding errors, flawed logic, faulty integrations, or unforeseen conditions not detected during development and testing.
Preventive Maintenance

In a software environment, technical debt, outdated libraries, or inefficient code can compound into outages and costly rework, so preventive improvements should be made early. Developers take preventive measures to anticipate and prevent potential incidents in preparation rather than waiting for them to arise and cause consequences. Typical tasks to do include refactoring high-risk modules, upgrading libraries/SDK, cleaning databases, conducting security enhancements, and optimizing performance hotspots.
Perfective Maintenance

Ongoing maintenance ensures a mobile app remains secure and functional, while regular updates and new features are essential to keep it relevant and competitive. That’s perfective maintenance. This type of work is about refining and enhancing an app based on user feedback, market insights, and evolving business objectives. For example, adding new payment methods, simplifying checkout flows, or revamping the design to match modern UI/UX standards. Perfective maintenance is no less important than other types. Developers who neglect this app maintenance strategy risk losing users to their rivals who continuously evolve their offerings.
Emergency Maintenance

This maintenance type is an urgent response to unexpected, critical failures that severely disrupt or disable the normal operation of a mobile application. For instance, a bug introduced by operating system updates, a server outage, or security vulnerabilities being exploited. Any of these can put an app to a standstill. Therefore, such issues demand immediate attention and rapid fixes. If not, they often involve high-severity crashes, security breaches, data corruption, or service outages.
Emergency maintenance is taken to restore the app’s functionality as quick as possible often with a temporary fix before being followed by a permanent solution. In some specific industries like fintech, healthcare, or ride-hailing, emergency maintenance are even more important as it influences safety, compliance, and financial risk.
Estimating How Much Mobile App Maintenance Typically Costs
Remember that the cheapest maintenance is guided by a well-thought-out plan and predictable budget. The goal is not to guess an exact figure but to make a grounded estimate of the cost, effort, and frequency required to keep your app updated.
Factors That “Move” the Numbers
Before you can put together real numbers behind maintenance, you must first be aware of the influencing factors that raise or lower your spending.
App Complexity & Size
It is a rule of thumb that a complex, large application with multifaceted features incurs significantly higher upkeep costs than a simple utility app. More screens, edge cases, and business rules demand more test surface to handle, larger codebases to refactor, more bug fixes, and more things to keep compatible.
Imagine you are running more checkout lanes in a store. You have more customers to serve, so you also need more staff to keep things moving smoothly. A prime example is an eCommerce app - it represents a high complexity use case due to its broad feature set, external integrations, and performance requirements.
Technology Used
The next factor is how many platforms your app supports. Native apps require separate maintenance tracks for iOS and Android, while cross-platform frameworks introduce unique compatibility challenges. Monolithic architectures tend to accumulate technical debt faster than modular or microservices-based designs, increasing refactoring and preventive maintenance efforts.
Supporting multiple platforms (iOS, Android, or cross-platform using frameworks like React Native and Flutter) causes maintenance costs to add up due to platform-specific updates.
Team Location & Rates
Similar to development, the maintenance costs fluctuate depending on labor markets and where your team sits. If you outsource app maintenance services, the vendor’s base of operations and staffing model will influence both the sticker prices (the listed hourly/monthly rate before add-ons or delays) and the effective cost of getting the work done. If your team/vendor is located in Vietnam, the cost can be up to 50% lower compared to the U.S. or Western Europe.
Update Frequency & Release Cadence
How often you release an update has a direct impact on the overall maintenance budget. In other words, consistent maintenance naturally demands more development, testing, and deployment resources, incurring higher costs. These are short-term expenditures. However, irregular, delayed, or ad-hoc updates can be even more expensive in the long run as they disrupt workflows and require rush efforts, not to mention increasing the chance of errors.
To spend smarter on long-term maintenance operations, you should adopt a consistent release rhythm. It can be weekly, bi-weekly, monthly, or quarterly depending on your business needs and user behaviors. If done strategically, a well-planned release cadence can optimize budget allocation and maintain user satisfaction over time.
Third-Party Dependencies & Integrations
Most mobile applications rely on third-party libraries, APIs, and external services. These integrations do speed up development and expand app’s functionality. For example, payment gateways, social logins, analytics, or cloud storage. Unfortunately, they also add more maintenance responsibilities as each dependency can change over time. APIs may be updated, pricing models may shift, and older libraries may become deprecated or replaced with alternatives. Whenever that happens, your app must be modified and retested to ensure compatibility. This means the maintenance cost increases accordingly.
Security & Compliance Requirements
Another cost driver lies in security assessment and remediation. Mobile applications must be patched frequently to address vulnerabilities, prevent data breaches, protect user data, and comply with evolving industry standards. Continuous audits and timely security updates cannot be overstated. Therefore, skimping on app security not only escalates long-term costs through potential fines or reputational damage but also puts existing users at risk.
Simple Steps to Estimate Your Maintenace Costs
Don’t forget that our goal is to build a realistic budget and avoid costly surprises or hidden expenses. Now, let’s break down the process into a few straightforward steps.

- Factoring in what can influence maintenance budgeting is an essential start. You can later break down expenses based on maintenance type, app complexity, and other related factors.
- Decide whether you’re budgeting only for bug fixes and OS updates or also for feature enhancements, performance improvements, and user support. A clear scope is the foundation for accurate estimates.
- Next, calculate the initial development cost - this serves as a baseline for further estimation. Maintaining a mobile app typically accounts for 15% - 20% of the original development cost per year. For example, when your app costs around $100,000 to build, you should budget $15,000 - $20,000 for annual maintenance.
- Estimate labor costs per month. You need to determine how many hours are needed monthly for fixing bugs, updating, and improving. Then multiply the number by average hourly rates of developers, testers, or whomever is involved.
- Adjust update cadence to fit your needs and user expectations. If your mobile app requires bi-weekly or monthly updates and security patches, you have to increase the percentage for annual maintenance toward the higher end - perhaps up to 25% of the initial build cost. If your app only needs regular app maintenance with minimal feature changes, the figure remains closer to 10% or 15%.
- Consider infrastructure and third-party services. Whether your app heavily depends on APIs, cloud storage, and external integrations, you should add a buffer of 5% - 10% for unexpected updates, pricing changes, or replacements.
- Include security and compliance costs. For regulated industries like finance, healthcare, education, etc., mobile apps also require periodic security patches, vulnerability scans, and compliance updates. This can add on to annual maintenance costs, pushing the percentage to 25% or 30% of the original development cost.
- Do not forget to set aside a contingency budget (10% - 15% of the total).
- Last but not least, sum all the components to have a total annual maintenance budget. Then, break it down into monthly amounts for easier planning.
Applying Effective Mobile Application Maintenance Practices
If you have a well-thought-out strategy for maintenance, you are one step closer to your goal of app longevity and user engagement. Let’s break it down into best practices.

Proceeding with a Structured Maintenance Plan
Efforts and resources must be allocated efficiently, so you need to have a plan. It is not only necessary to keep technical goals aligned with business priorities but also ensure budgeting consistency, and prevents reactive “firefighting.” Without a proper plan, costs can spiral and maintenance becomes fragmented.
- It defines the scope of maintenance, including bug fixes, OS updates, new features, security patches, and performance optimization.
- It sets a predictable release schedule that ensures systematic updates and enhancements are made. For example, weekly, bi-weekly, monthly, or quarterly. You should consider scheduling updates during off-peak hours to minimize user disruption and maximize uptime.
Continuous Monitoring & Reporting
Regular performance monitoring plus structured reporting allows your team to collect real-time insights, thereby detecting issues early and taking proactive measures to maintain app stability and improve user retention.
Key metrics such as load times, responsiveness, crash rates, and user flows, can be tracked automatically using collect app data using analytics and monitoring tools. Firebase, Crashlytics, or New Relic are a few popular options that streamline the process of gathering and analyzing app data for timely action.
Prioritizing Security
The next best practice is to always treat security as an ongoing responsibility, not episodic. Your team needs to conduct routine audits, apply patches promptly, and prepare for evolving compliance requirements and implicit vulnerabilities.
Remember that consistent attention to app security protects not only users but also brand reputation. Moreover, regular reporting on the app’s security status should be a part of your monitoring cycle as well. This ensures leadership is aware of both risks involved and investments needed to address issues (if any).
Incorporating User Feedback
Effective maintenance does not stop at optimizing technical performance but to listen to active users. User reviews, surveys, and support tickets are invaluable for identifying pain points and perusing user expectations.
Constructive feedback from people who actually experience the app helps you prioritize fixes and enhancements that matter the most to users. So, you should create a user feedback loop that informs your maintenance plan. Also, proactive communication with users can foster trust. It will be useful if you aim at better app store rankings.
Setting a Predictable Schedule
Mobile apps that evolve steadily remain far more competitive, and nothing frustrates users more than unexpected downtime or erratic maintenance. While ad-hoc updates are sometimes inevitable, especially when it comes to urgent bug fixes or critical patches, they should not become the norm.
Instead, the maintenance team should adopt a predictable cadence, such as monthly or quarterly, and communicate it clearly to your users. A consistent schedule ensures strong commitment while reducing churn and the risk of accumulating technical debt.
Outsourcing to a Mobile App Maintenance Company If Necessary
Most businesses prefer to manage maintenance internally. But in reality, you need to know when to outsource part or all of maintenance and when to keep all done in house. So, when will outsourcing make sense?
Maybe your roadmap team is stretched thin, and you need a steady hand on OS or SDK churn. Perhaps you want broader device coverage, 24/7 triage, or a faster path to a mature CI/CD pipeline. Or maybe you’ve inherited a legacy codebase that requires stabilization before new features can land safely. In these scenarios, outsourcing allows you to maintain consistency, avoid costly disruptions, and free your team to concentrate on strategic initiatives instead of day-to-day upkeep.
There are good reasons to collaborate with a service provider for maintenance services. However, outsourcing does not replace your internal team; instead, it extends its capabilities. If done right, outsourcing maintenance can help you ensure that your application remains reliable, secure, and competitive over the long term.
Orient Software - the Trusted Partner for Mobile App Development & Maintenance Services
Above all, remember that the most expensive maintenance is the instability that you do not notice or overlook until real consequences occur, like churned users or poor app store rankings. A successful mobile application is not simply with a stunning user interface, seamless user experience, or features catered to user needs; it’d better be a well-maintained app.
Performance monitoring is needed to keep your mobile solution fast, stable, and up to date, but it is not enough without ongoing app maintenance. Whether you plan to build an internal maintenance capability or entrust it with a reliable vendor, this checklist is an important, foundational step that you can always start with.

In addition to providing a checklist, Orient Software offers you professional support as a technical partner for not only mobile app support and maintenance services but also custom development and staffing solutions. Let Orient Software accompany you on your mobile app journey toward success that lasts. Share your mobile application or your upcoming project with us, and we will help you turn your vision into fruition.


















